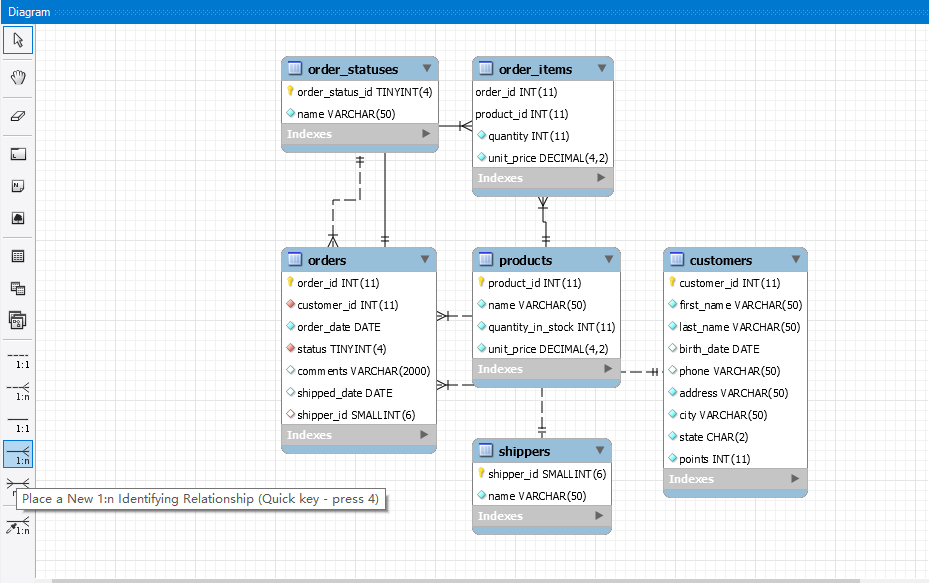
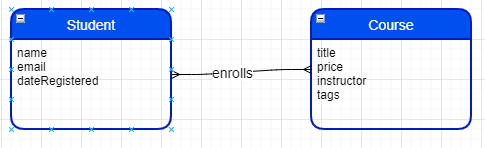
# ER DigramMySQL Workbench 可以生成数据表的 Entity RelationShip Digram. Menu Path: Database -> Reverse Engineer -> 选择相关 Database 生成 Model Digram.
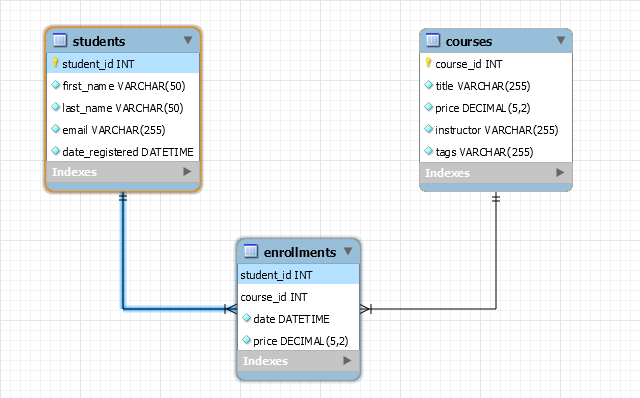
如下是 sql_store 的 ER Digram.
notes: Identifying relationships exist when the primary key of the parent entity is included in the primary key of the child entity. On the other hand, a non-identifying relationship exists when the primary key of the parent entity is included in the child entity but not as part of the child entity’s primary key.
当父实体的主键包含在子实体的主键中时,存在标识关系。另一方面,如果父实体的主键包含在子实体中,但不作为子实体的主键的一部分,则存在非标识关系。
# Notes# All clauses other than Select are optionalSelect 以外的子句都是可选的
# Field values are case insensitive by default栏位值默认不区分大小写
1 select * from customers where state = 'va' ;
customer_id
first_name
last_name
birth_date
phone
address
city
state
points
2
Ines
Brushfield
1986-04-13
804-427-9456
14187 Commercial Trail
Hampton
VA
947
1 2 3 select * from customers where birth_date > '1990-01-01' ;
# Varchar vs Charname varchar (50) 如果 name 只有 5 个字符那么 varchar (50) 只使用 5 个字符,不会浪费空间;
name char (50) 如果 name 只有 5 个字符会插入 45 个空白字符填满到 50 个字符。
# Defaultdefault 表示让 mysql 生成这个值,可以用于主键自增栏位和有默认值的栏位
1 2 3 4 5 6 insert into customersvalues (default , 'babb' , 'chen' , default , default , '18896763538' , 'henan' , 'xy' , default );update customers set points = default where customer_id = 1 ;
# Insert Multi Rows1 2 3 4 insert into shippers (name)values ('Shipper1' ), ('Shipper2' ), ('Shipper3' );
# Insert Multi Tables1 2 3 4 5 6 insert into orders (customer_id, order_date, status)values (1 , '2010-02-02' , 1 );insert into order_itemsvalues (last_insert_id(), 1 , 1 , 2.95 ), (last_insert_id(), 2 , 1 , 3.95 );
# Regexp查询 last_name 包含 field|mac|rose 的数据
1 2 3 select * from customers where last_name regexp 'field|mac|rose' ;
查询 last_name 包含 ge|ie|me 的数据
1 2 3 select * from customers where last_name regexp '[gim]e' ;
查询 last_name 以 b 开头且包含 ge|ie|me 的数据
1 2 3 select * from customers where last_name regexp '^b.*?[gim]e' ;
# Limit跳过前 6 条记录,然后获取 3 条记录
1 2 3 select * from customers limit 6 , 3 ;
# Order默认状态下 group by 会按照其指定的列排序会影响性能,所以查询或 view 中应尽量避免使用 group by
1 2 3 select client_id, sum (invoice_total) as total_sales from invoices group by client_id;
client_id
total_sales
1
802.89
2
101.79
3
705.90
5
980.02
# Aggregate Function1 2 3 4 use sql_invoicing; select * from sql_invoicing.invoices;
invoice_id
number
client_id
invoice_total
payment_total
invoice_date
due_date
payment_date
1
91-953-3396
2
101.79
0.00
2019-03-09
2019-03-29
2
03-898-6735
5
175.32
8.18
2019-06-11
2019-07-01
2019-02-12
3
20-228-0335
5
147.99
0.00
2019-07-31
2019-08-20
4
56-934-0748
3
152.21
0.00
2019-03-08
2019-03-28
5
87-052-3121
5
169.36
0.00
2019-07-18
2019-08-07
6
75-587-6626
1
157.78
74.55
2019-01-29
2019-02-18
2019-01-03
7
68-093-9863
3
133.87
0.00
2019-09-04
2019-09-24
8
78-145-1093
1
189.12
0.00
2019-05-20
2019-06-09
9
77-593-0081
5
172.17
0.00
2019-07-09
2019-07-29
10
48-266-1517
1
159.50
0.00
2019-06-30
2019-07-20
11
20-848-0181
3
126.15
0.03
2019-01-07
2019-01-27
2019-01-11
13
41-666-1035
5
135.01
87.44
2019-06-25
2019-07-15
2019-01-26
15
55-105-9605
3
167.29
80.31
2019-11-25
2019-12-15
2019-01-15
16
10-451-8824
1
162.02
0.00
2019-03-30
2019-04-19
17
33-615-4694
3
126.38
68.10
2019-07-30
2019-08-19
2019-01-15
18
52-269-9803
5
180.17
42.77
2019-05-23
2019-06-12
2019-01-08
19
83-559-4105
1
134.47
0.00
2019-11-23
2019-12-13
# max, avg, sum, countmax, min, avg, sum, count 等聚合函数会忽略 null 的记录,聚合栏位前添加 distinct 可以排除重复记录
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 select max (invoice_total) as highest, min (invoice_total) as lowest, avg (invoice_total) as average, sum (invoice_total) as total, count (invoice_total) as number_of_invoices, count (payment_date) as number_of_payments, count (* ) as total_records, count (client_id) as number_of_clients, count (distinct client_id) as number_of_distinct_clients from invoices;
highest
lowest
average
total
number_of_invoices
number_of_payments
total_records
number_of_clients
number_of_distinct_clients
189.12
101.79
152.388235
2590.60
17
7
17
17
4
# rollup根据 group by 栏位分层归纳汇总
1 2 3 4 select client_id, sum (invoice_total) as total_sales from invoices group by client_id with rollup ;
client_id
total_sales
1
802.89
2
101.79
3
705.90
5
980.02
2590.60
1 2 3 4 5 6 select state, city, sum (invoice_total) as total_sales from invoices i join clients using (client_id) group by state, city with rollup ;
state
city
total_sales
CA
San Francisco
705.90
CA
705.90
NY
Syracuse
802.89
NY
802.89
OR
Portland
980.02
OR
980.02
WV
Huntington
101.79
WV
101.79
2590.60
# Common Use Function# numericrand () 返回 0 - 1 之间的随机数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 SELECT ROUND(5.73 ), ROUND(5.73 , 1 ), TRUNCATE (5.73 , 1 ), CEILING (5.73 ), FLOOR (5.73 ), RAND();
round(5.73)
round(5.73, 1)
truncate(5.73, 1)
ceiling(5.73)
floor(5.73)
rand()
6
5.7
5.7
6
5
0.27181225481611887
# string1 2 3 4 5 6 7 select upper ('sky' ) a, lower ('Sky' ) b, ltrim(' sky' ) c, rtrim('sky ' ) d, trim (' sky ' ) e, left ('babb chen' , 4 ) f, right ('babb chen' , 4 ) g, substring ('babb chen' , 6 , 4 ) h, locate('c' , 'babb chen' ) i, locate('chen' , 'babb chen' ) j, replace('babb chen' , 'babb' , 'bob' ) k, concat('babb' , 'chen' ) l;
a
b
c
d
e
f
g
h
i
j
k
l
SKY
sky
sky
sky
sky
babb
chen
chen
6
6
bob chen
babbchen
# date1 select now(), curdate(), curtime();
now()
curdate()
curtime()
2020-09-12 16:02:08
2020-09-12
16:02:08
1 select year (now()), month (now()), day (now()), hour (now()), minute (now()), second (now());
year(now())
month(now())
day(now())
hour(now())
minute(now())
second(now())
2020
9
12
16
4
53
extract 也可 b 以用来提取日期的一部分,并且 extract 是 sql 标准的一部分
1 2 3 4 5 6 select extract (year from now()) as year , extract (month from now()) as month , extract (day from now()) as day , extract (hour from now()) as hour , extract (minute from now()) as minute , extract (second from now()) as second ;
year
month
day
hour
minute
second
2020
9
12
16
9
27
1 2 3 4 5 select date_format(now(), '%Y-%m-%d %H:%i %p' ) as date ;date 2020 -09 -12 16 :14 PM
日期的相关计算
MySQL 在执行查询语句时,会先对 SELECT 子句里的列表进行扫描,并对列进行计算,所以 (select datediff (tomorrow, yesterday)) as datediff 可以正确运行
1 2 3 4 select date_add(now(), interval 1 day ) as tomorrow, date_sub(now(), interval 1 day ) as yesterday, (select datediff(tomorrow, yesterday)) as datediff, time_to_sec('09:00' ) - time_to_sec('09:02' ) as secdiff;
tomorrow
yesterday
datediff
secdiff
2020-09-13 16:35:38
2020-09-11 16:35:38
2
-120
# nullcoalesce 返回多个值中的第一个非 null 值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 select ifnull(null , 'unknown' ) column_a, ifnull('a' , 'unknown' ) column_b, coalesce (null , null , null , 'b' ) column_c, coalesce (null , 'a' , 'b' ) column_d; column_a column_b column_c column_d unknown a b a
# case1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 select order_id, if(year (order_date) = year (now()), 'Active' , 'Archived' ) as category from orders; select order_id, case when year (order_date) = year (now()) then 'Active' when year (order_date) = year (now()) - 1 then 'Last Year' when year (order_date) < year (now()) - 1 then 'Archived' else 'Future' end as category from orders;
# Viewupdateable view
可更新视图是指不包含 distinct,aggregate function (min,max, sum, min, max),group by, having,union 的视图,可以执行 update,insert,delete 操作。通过 view 更新数据可能导致更新后的数据从 view 中删除,可以添加 with check option 子句防止行消失
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 create or replace view invices_with_balance as select invoice_id, number, client_id, invoice_total, payment_total, invoice_total - payment_total as balance, invoice_date, due_date, payment_date from invoices where (invoice_total - payment_total) > 0 with check option; select * from invices_with_balance;
invoice_id
number
client_id
invoice_total
payment_total
balance
invoice_date
due_date
payment_date
1
91-953-3396
2
101.79
0.00
101.79
2019-03-09
2019-03-29
2
03-898-6735
5
175.32
8.18
167.14
2019-06-11
2019-07-01
2019-02-12
…
执行如下 sql 会 产生 Error Code: 1369. CHECK OPTION failed ‘sql_invoicing.invices_with_balance’, 因为更新之后 invoice_total - payment_total = 0 ,不满足大于 0 的条件会导致 invoice_id = 1 的数据从 view 中移除。
1 2 3 update invices_with_balance set payment_total = invoice_total where invoice_id = 1 ;
# Procedure1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 delimiter $$ drop procedure if exists get_unpaid_invoices_for_client;create procedure get_unpaid_invoices_for_client( client_id int , out invoices_count int , out invoices_total decimal ) begin select count (* ), sum (invoice_total) into invoices_count, invoices_total from invoices i where i.client_id = client_id and i.payment_total = 0 ; end $$delimiter ; set @invoices _count = 0 ;set @invoices _total = 0 ;call get_unpaid_invoices_for_client(5 , @invoices _count, @invoices _total);select @invoices _count, @invoices _total;@invoices _count @invoices _total3 490
# Function1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 delimiter $$ drop function if exists get_risk_factor_for_client;create function get_risk_factor_for_client(client_id int )returns integer reads sql data begin declare risk_factor decimal (9 , 2 ) default 0 ; declare invoices_total decimal (9 , 2 ); declare invoices_count int ; select count (* ), sum (invoice_total) into invoices_count, invoices_total from invoices where client_id = client_id; set risk_factor = invoices_total / invoices_count * 5 ; return ifnull(risk_factor, 0 ); end $$delimiter ; select client_id, name, get_risk_factor_for_client(client_id) as risk_factor from clients;
# Event开启 event_scheduler
1 2 show variables like 'event%' ;set global event_scheduler = on ;
定义 event
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 delimiter $$ drop event if exists yearly_delete_stale_audit_rows;create event yearly_delete_stale_audit_rowson schedule every 1 year starts '2019-01-01' ends '2029-01-01' do begin delete from payment_audit where action_date < now() - interval 1 year ; end $$delimiter ;
查看 event
1 2 show events;show events like 'yearly%' ;
DB
Name
Definer
Time zone
Type
Execute at
Interval value
Interval field
Starts
Ends
Status
Originator
character_set_client
collation_connection
Database Collation
sql_invoicing
yearly_delete_stale_audit_rows
root@localhost
SYSTEM
RECURRING
1
YEAR
2019-01-01 00:00:00
2029-01-01 00:00:00
ENABLED
1
utf8mb4
utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
utf8_general_ci
启用禁用 event
1 2 alter event yearly_delete_stale_audit_rows disable;alter event yearly_delete_stale_audit_rows enable;
# Transactionsautocommit
每执行一条语句,MySQL 会将该语句放在事务中,如果没有错误,会自动提交
1 2 3 4 5 show variables like 'autocommit' ;Variable_name Value autocommit ON
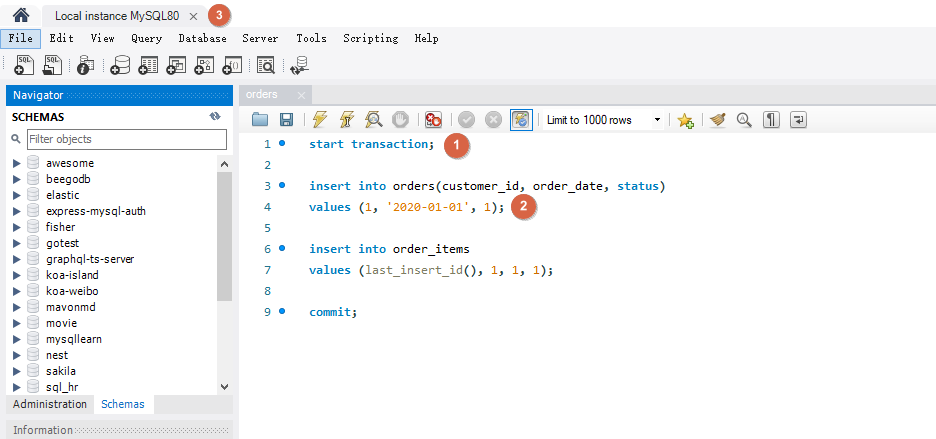
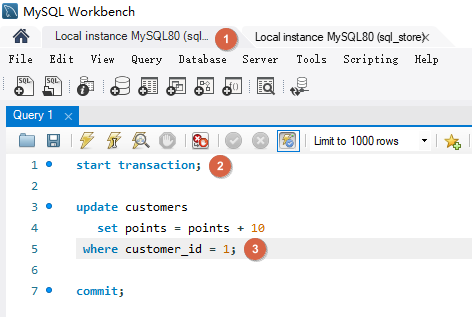
创建 transaction
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 start transaction; insert into orders(customer_id, order_date, status)values (1 , '2020-01-01' , 1 ); insert into order_itemsvalues (last_insert_id(), 1 , 1 , 1 ); commit ;
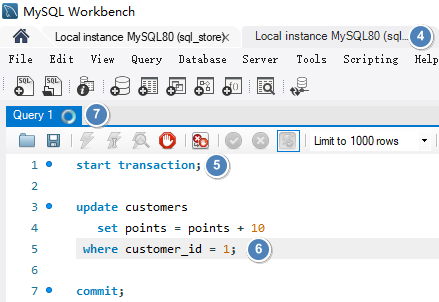
模拟执行到 insert into order_items 时断开 server 连接。
Workbench 菜单 Query -> Excute Current Statement (Ctrl + Enter) 执行 1, 2, 关闭连接,重新连接查询 orders 数据没有被插入。
# Concurrency and Locking1 select * from customers where customer_id = 1 ;
customer_id
first_name
last_name
birth_date
phone
address
city
state
points
1
Babara
MacCaffrey
1986-03-28
781-932-9754
0 Sage Terrace
Waltham
MA
2303
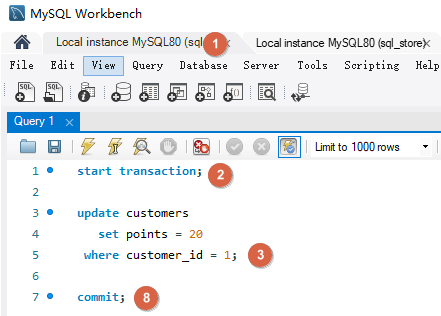
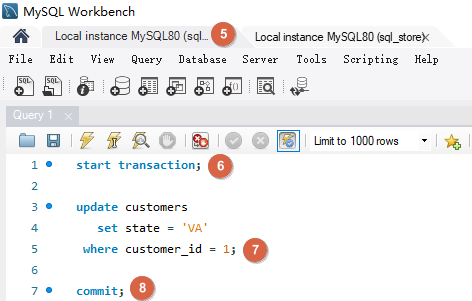
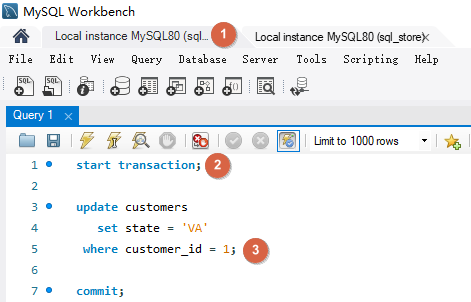
如下在第一个连接中将客户的积分加 10 但是没有提交。在第二个连接中同样执行将客户的积分加 10 的操作,此时会等待第一个连接操作的 commit 或 rollback.
Connection One
Connection Two
将第一个操作 commit 之后,第二个也进行 commit, 如下客户 customer_id 为 1 的积分会增加 20。
customer_id
first_name
last_name
birth_date
phone
address
city
state
points
1
Babara
MacCaffrey
1986-03-28
781-932-9754
0 Sage Terrace
Waltham
MA
2323
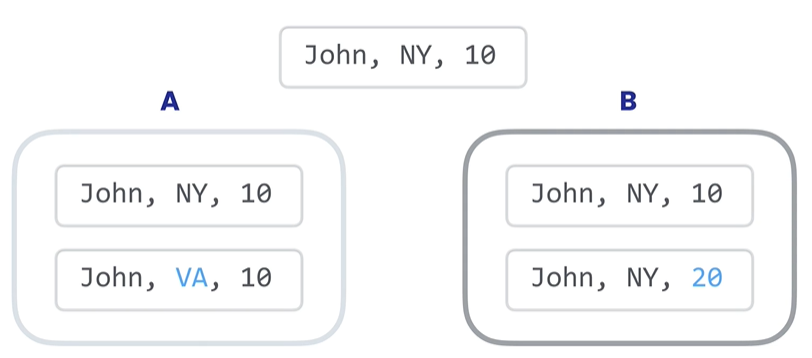
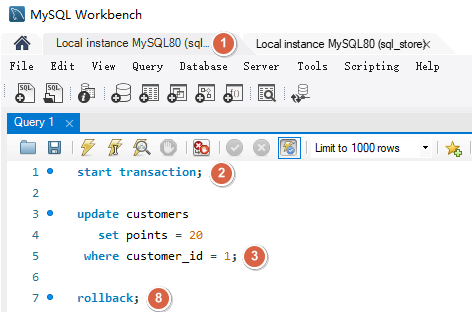
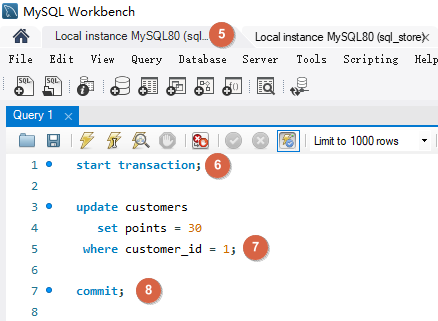
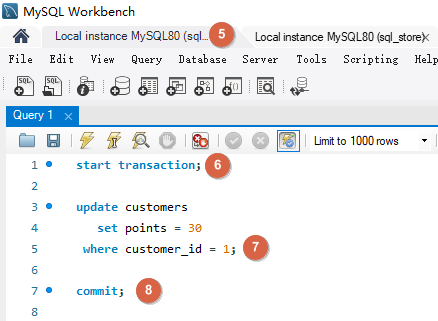
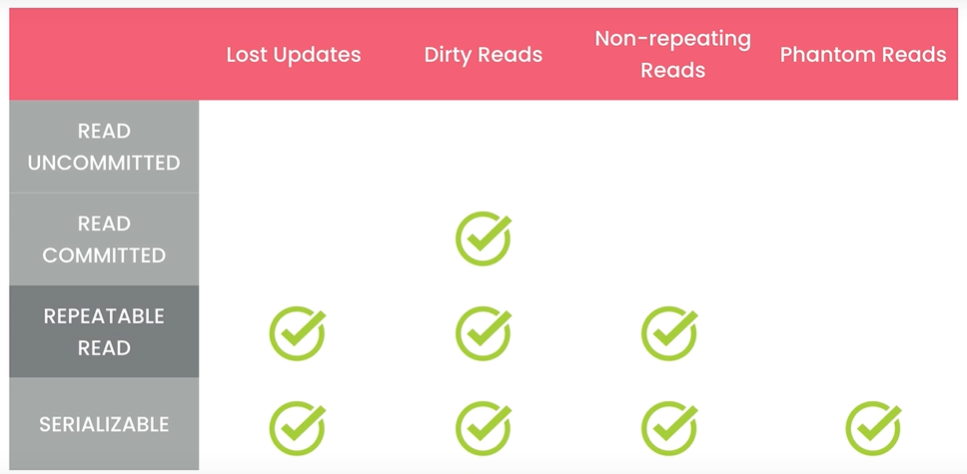
# Lost Updates当两个事务尝试更新相同的数据并且没有上锁时,就会发生这种情况,较晚提交的事务会覆盖较早事务做的更改。
如下事务 A 和事务 B 对同一数据修改,如果事务 B 更晚提交就会覆盖事务 A 的提交,事务 A 的更新就会丢失。解决方法是使用锁。默认情况下 MySQL 会使用锁定机制。防止两个事务同时更新同样的数据。它们会一个一个按照顺序执行,这样连个更新都能完成。
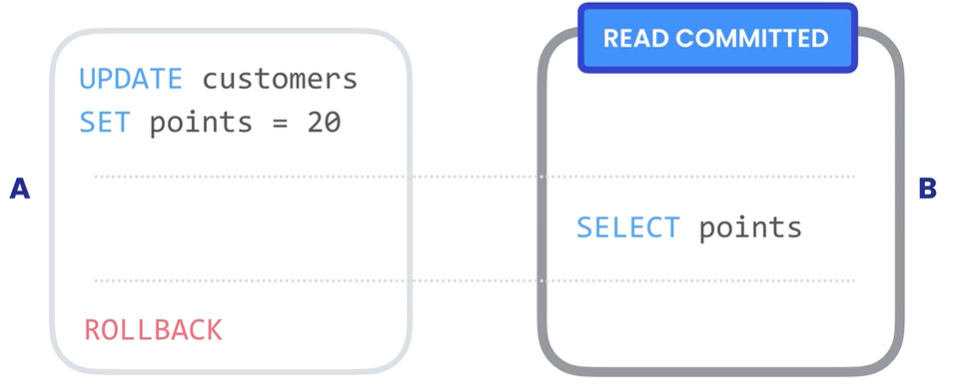
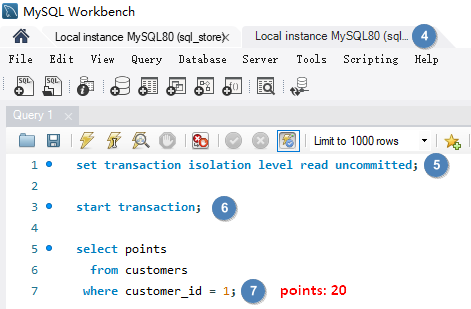
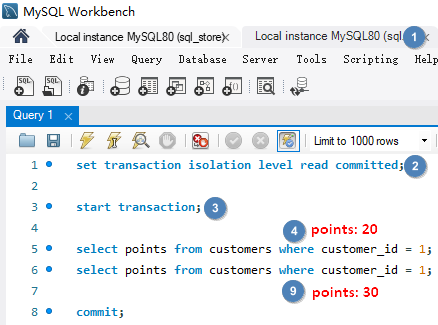
# Dirty Reads脏读就是一个事务读取了尚未被提交的数据。事务 B 读取了事务 A 尚未提交的数据,并基于数据做了决策(每点积分给予 1% 折扣),但是之后事务 A 又进行了回滚,实际客人没有 20 积分,事务 B 却给了 20 % 折扣。解决此问题需要为事务建立隔离级别 READ COMMITTED,这样事务就只能读取已经提交的数据。
Connection One
Connection Two
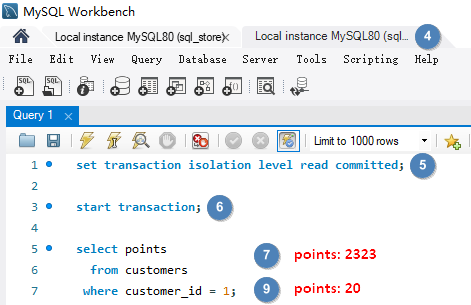
使用隔离级别 READ COMMITTED set transaction isolation level read committed; 解决 Dirty Reads。
Connection One
Connection Two
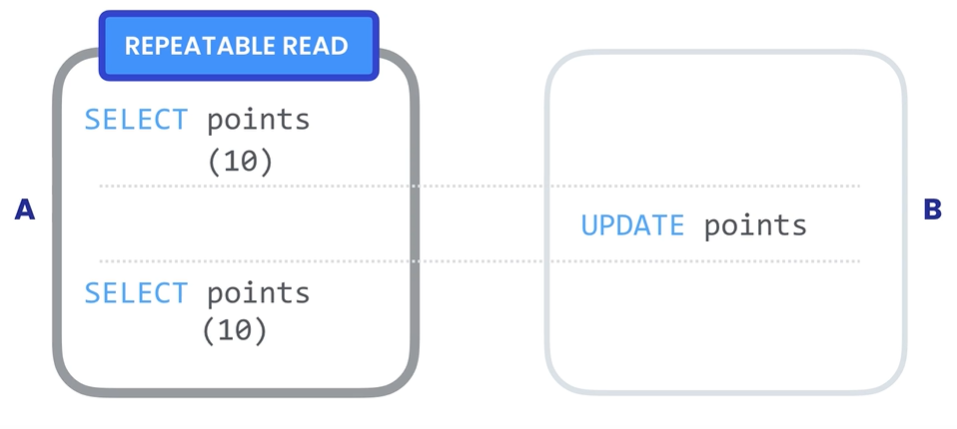
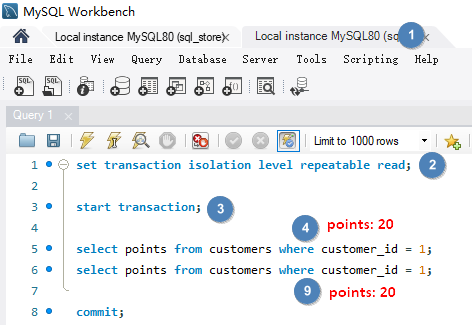
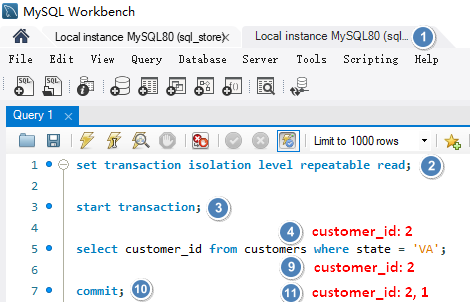
# Non-repeating Reads不可重复读就是在事务过程中读取了某个数据两次,得到了不同结果。解决此问题需要为事务建立隔离级别 REPEATABLE READ, 将它与其他事务隔离,确保数据更改对事务不可见,读取的数据是可重复和一致的,即使其它事务更改了数据,我们会看到首次读取就创建的快照。
Connection One
Connection Two
使用隔离级别 REPEATABLE READ set transaction isolation level repeatable read 解决 Non-repeating Reads。
Connection One
Connection Two
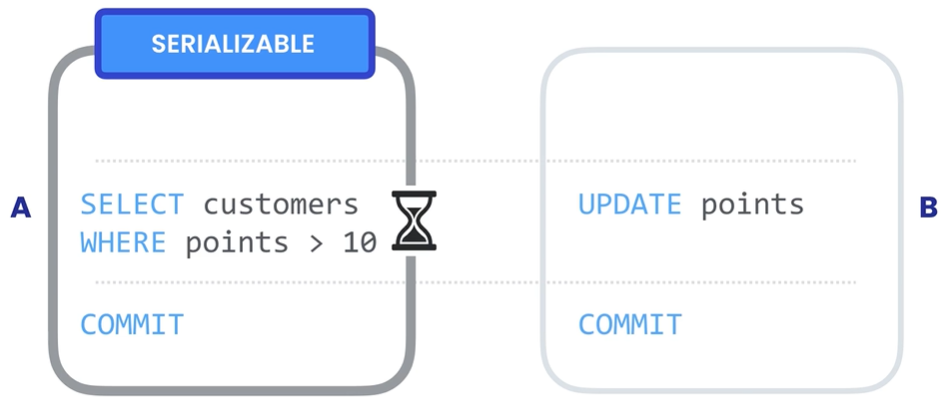
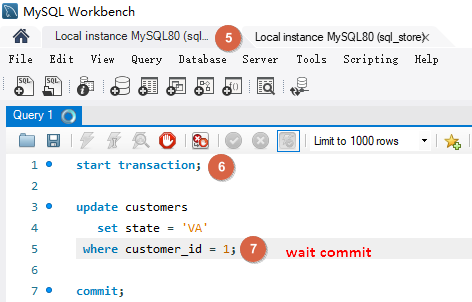
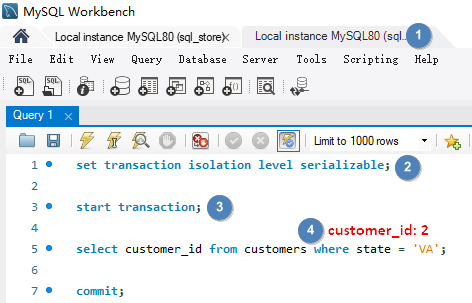
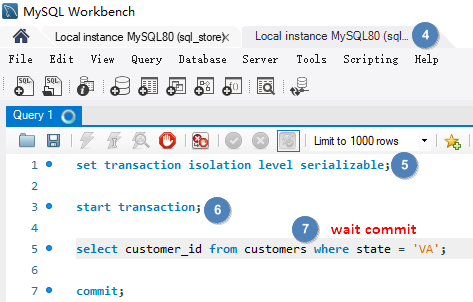
# Phantom Reads幻读是指在事务执行查询之后进行了添加,更新或删除,实际读取的是添加,更新或删除之前的数据,事务执行完成之后仍然有符合条件的数据,这种突然出现的数据就像幽灵 👻 一样。解决此问题需要为事务建立隔离级别 SERIALIZABLE, 它能保证当有别的事务在更新数据时,我们的事务能够知晓变动,如果有其它事务修改了可能影响查询结果的数据,我们的事务必须等待它们完成。这是事务的最高隔离级别,保证最大的确定性,但是会影响性能。
Connection One
Connection Two
使用隔离级别 SERIALIZABLE set transaction isolation level serializable 解决 Phantom Reads。
Connection One
Connection Two
更高的隔离级别意味着更低的并发问题,但同时也意味着更多的锁和过呢更低的并发性能。
MySQL 的默认隔离级别时 REPEATABLE READ
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 show variables like 'transaction_isolation' ;Variable_name Value transaction_isolation REPEATABLE- READ set session transaction isolation level serializable;set global transaction isolation level serializable;
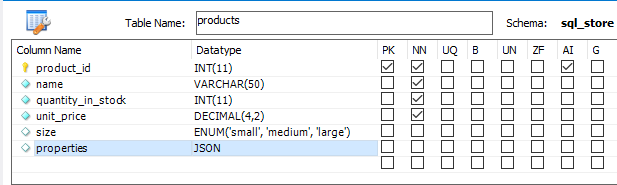
# Datatype# jsonjson raw string
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 update products set properties = ' { "dimensions": [1, 2, 3], "weight": 10, "manufactor": { "name": "sony" } } ' where product_id = 1 ;select * from products where product_id = 1 ;
product_id
name
quantity_in_stock
unit_price
size
properties
1
Foam Dinner Plate
70
1.21
small
{“weight”: 10, “dimensions”: [1, 2, 3], “manufactor”: {“name”: “sony”}}
json_object, json_array
1 2 3 4 5 6 update products set properties = json_object ( 'weight' , 10 , 'dimensions' , json_array (1 , 2 , 3 ), 'manufactor' , json_object ('name' , 'sony' ) ) where product_id = 1 ;
json_extract
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 select json_extract(properties, '$.weight' ) as extract_weight, properties - > '$.weight' as weight, properties - > '$.dimensions[0]' as x, properties - > '$.dimensions[1]' as y, properties - > '$.dimensions[2]' as z, properties - > '$.manufactor.name' as manufactor_in_quotes, properties - >> '$.manufactor.name' as manufactor from products where properties - >> '$.manufactor.name' = 'sony' ;
extract_weight
weight
x
y
z
manufactor_in_quotes
manufactor
10
10
1
2
3
“sony”
sony
json_set
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 update products set properties = json_set( properties, '$.weight' , 20 , '$.age' , 10 ) where product_id = 1 ;
json_remove
1 2 3 4 5 6 update products set properties = json_remove( properties, '$.age' ) where product_id = 1 ;
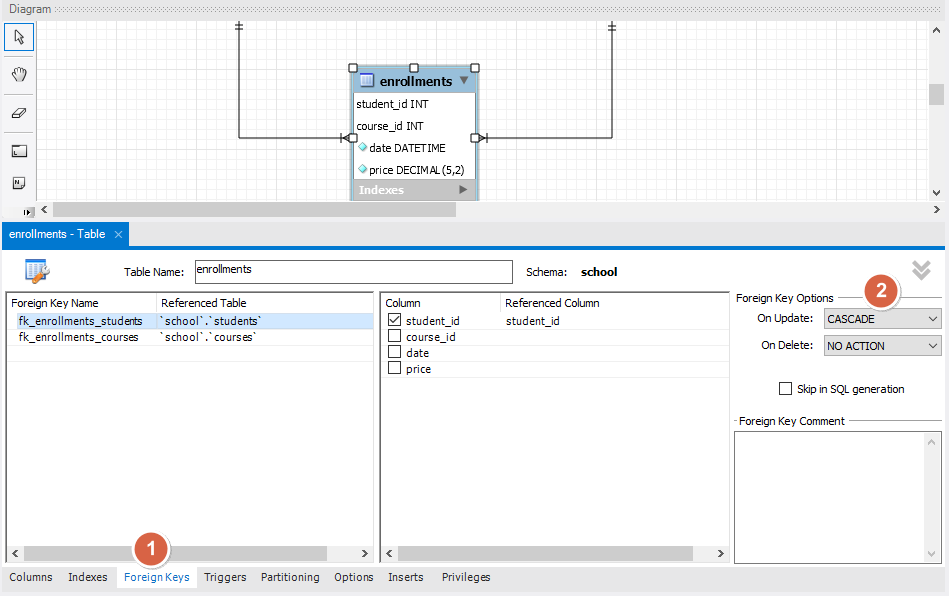
# Data Modelling# conceptual modelRepresents the entities and their relationships. Generally use ER(Entity Relationship) Digram or UML
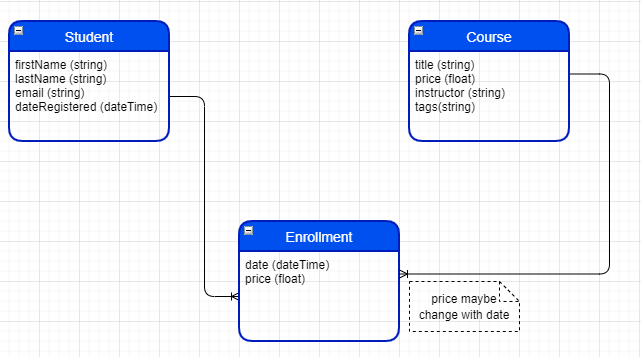
# logic modelLogic model is independent of database technologics. It’s just an abstract data model that clearly shows our entities. But there’s something more detailed than the conceptual model.
# physic modelFile -> New Model
Add Diagram
Add Tables and Columns
Add Primary Key, Foreign Key and Relationship
Setting Foreign Key,CASCADE on update, NO ACTION(RESTRICT) on delete (reject delete)