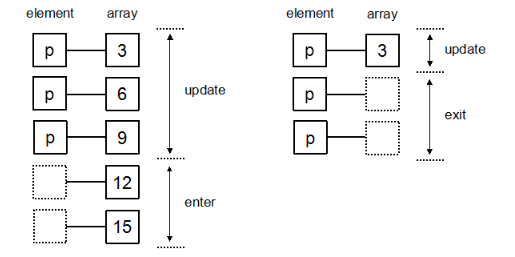
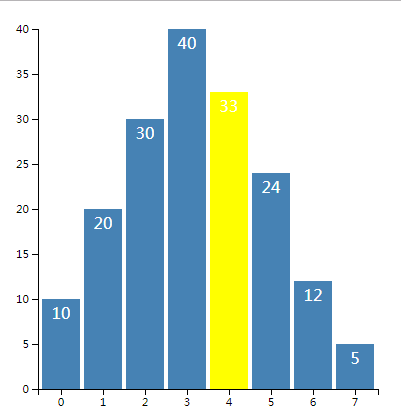
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
| <html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<title>交互式操作</title>
</head>
<style>
.axis path,
.axis line {
fill: none;
stroke: black;
shape-rendering: crispEdges;
}
.axis text {
font-family: sans-serif;
font-size: 11px;
}
.MyRect {
}
.MyText {
fill: white;
text-anchor: middle;
}
</style>
<body>
<script src="http://d3js.org/d3.v3.min.js" charset="utf-8"></script>
<script>
var width = 400
var height = 400
var svg = d3
.select('body')
.append('svg')
.attr('width', width)
.attr('height', height)
var padding = {
left: 30,
right: 30,
top: 20,
bottom: 20
}
var dataset = [10, 20, 30, 40, 33, 24, 12, 5]
var xScale = d3.scale
.ordinal()
.domain(d3.range(dataset.length))
.rangeRoundBands([0, width - padding.left - padding.right])
var yScale = d3.scale
.linear()
.domain([0, d3.max(dataset)])
.range([height - padding.top - padding.bottom, 0])
var xAxis = d3.svg
.axis()
.scale(xScale)
.orient('bottom')
var yAxis = d3.svg
.axis()
.scale(yScale)
.orient('left')
var rectPadding = 4
var rects = svg
.selectAll('.MyRect')
.data(dataset)
.enter()
.append('rect')
.attr('class', 'MyRect')
.attr(
'transform',
'translate(' + padding.left + ',' + padding.top + ')'
)
.attr('x', function(d, i) {
return xScale(i) + rectPadding / 2
})
.attr('y', function(d) {
return yScale(d)
})
.attr('width', xScale.rangeBand() - rectPadding)
.attr('height', function(d) {
return height - padding.top - padding.bottom - yScale(d)
})
.attr('fill', 'steelblue')
.on('mouseover', function(d, i) {
d3.select(this).attr('fill', 'yellow')
})
.on('mouseout', function(d, i) {
d3.select(this)
.transition()
.duration(500)
.attr('fill', 'steelblue')
})
var texts = svg
.selectAll('.MyText')
.data(dataset)
.enter()
.append('text')
.attr('class', 'MyText')
.attr(
'transform',
'translate(' + padding.left + ',' + padding.top + ')'
)
.attr('x', function(d, i) {
return xScale(i) + rectPadding / 2
})
.attr('y', function(d) {
return yScale(d)
})
.attr('dx', function() {
return (xScale.rangeBand() - rectPadding) / 2
})
.attr('dy', function(d) {
return 20
})
.text(function(d) {
return d
})
svg
.append('g')
.attr('class', 'axis')
.attr(
'transform',
'translate(' + padding.left + ',' + (height - padding.bottom) + ')'
)
.call(xAxis)
svg
.append('g')
.attr('class', 'axis')
.attr(
'transform',
'translate(' + padding.left + ',' + padding.top + ')'
)
.call(yAxis)
</script>
</body>
</html>
|